$ cat abspath.sh
#!/bin/sh
echo $(cd $(dirname $0) && pwd)/$(basename $0)
2011/07/31
2011/07/25
android tips: what to do before install self-compiled apk
yaboo@maniac:~/Projects/Android/UseLocation$ jarsigner -verbose -keystore ~/.android/debug.keystore bin/MainActivity-unsigned.apk androiddebugkey キーストアのパスワードを入力してください: 追加中: META-INF/MANIFEST.MF 追加中: META-INF/ANDROIDD.SF 追加中: META-INF/ANDROIDD.RSA 署名中: res/layout/main.xml 署名中: AndroidManifest.xml 署名中: resources.arsc 署名中: res/drawable-hdpi/icon.png 署名中: res/drawable-ldpi/icon.png 署名中: res/drawable-mdpi/icon.png 署名中: classes.dex
android tips: check build-target from android-sdk command
first, check installed android-sdk supports my build-target.
now, create android project using 'android' command
yaboo@maniac:~/Projects/Android$ android list targets
Available Android targets:
id: 1 or "android-3"
Name: Android 1.5
Type: Platform
API level: 3
Revision: 4
Skins: QVGA-P, HVGA-L, QVGA-L, HVGA-P, HVGA (default)
id: 2 or "android-4"
Name: Android 1.6
Type: Platform
API level: 4
Revision: 3
Skins: WVGA800 (default), WVGA854, QVGA, HVGA
id: 3 or "android-7"
Name: Android 2.1-update1
Type: Platform
API level: 7
Revision: 2
Skins: WQVGA400, WVGA800 (default), WVGA854, QVGA, WQVGA432, HVGA
id: 4 or "android-8"
Name: Android 2.2
Type: Platform
API level: 8
Revision: 2
Skins: WQVGA400, WVGA800 (default), WVGA854, QVGA, WQVGA432, HVGA
id: 5 or "android-9"
Name: Android 2.3.1
Type: Platform
API level: 9
Revision: 2
Skins: WQVGA400, WVGA800 (default), WVGA854, QVGA, WQVGA432, HVGA
id: 6 or "android-10"
Name: Android 2.3.3
Type: Platform
API level: 10
Revision: 1
Skins: WQVGA400, WVGA800 (default), WVGA854, QVGA, WQVGA432, HVGA
id: 7 or "android-11"
Name: Android 3.0
Type: Platform
API level: 11
Revision: 1
Skins: WXGA (default)
id: 8 or "android-12"
Name: Android 3.1
Type: Platform
API level: 12
Revision: 2
Skins: WXGA (default)
id: 9 or "android-13"
Name: Android 3.2
Type: Platform
API level: 13
Revision: 1
Skins: WXGA (default)
now, create android project using 'android' command
yaboo@maniac:~/Projects/Android$ android create project --target 6 --path ./myProject --activity MyActivity --package com.yablog.myproject Created project directory: ./myProject Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/src/com/yablog/myproject Added file ./myProject/src/com/yablog/myproject/MyActivity.java Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/res Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/bin Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/libs Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/res/values Added file ./myProject/res/values/strings.xml Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/res/layout Added file ./myProject/res/layout/main.xml Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/res/drawable-hdpi Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/res/drawable-mdpi Created directory /home/yaboo/Projects/Android/myProject/res/drawable-ldpi Added file ./myProject/AndroidManifest.xml Added file ./myProject/build.xml Added file ./myProject/proguard.cfg
2011/07/24
python tips: convert ip-address returned by android api to readable format
In SL4A, wifiGetConnectionInfo contains ip-address of an android device. But it is formatted in integer, difficult to understand. Below script can convert integer formatted ip-addr to human-friendly format 8^)
>>> ip = 67807424
>>> format(ip, 'b')
'100000010101010100011000000'
>>> len(format(ip, 'b'))
27
>>> ipstr = '00000' + format(ip, 'b')
>>> L = []
>>> for i in range(0, 32, 8):
... L.append(str(int(ipstr[i:i+8], 2)))
...
>>> L.reverse()
>>> L
['192', '168', '10', '4']
>>> ('.').join(L)
'192.168.10.4'
python tips: python scripting on android and remotecontrol
* Overview
SL4A(Script Layer for Android) enables you to execute several script language (such as python, ruby, ...) on your android devices. Today I tried to SL4A and remotecontrol which enables you to remotely execute python code from your non-android computer (such as linux, windows...).
- SL4A installation steps are introduced here
- RemoteControl setup steps are described here
- SL4A API is also described here
* Get location and geocode from android device (RemoteControl)
* Testing TelephonyManager functionality
* Testing Batterymanager API
* Testing CommonIntentsFacade
* Testing ContactsFacade
* Testing WifiFacade
SL4A(Script Layer for Android) enables you to execute several script language (such as python, ruby, ...) on your android devices. Today I tried to SL4A and remotecontrol which enables you to remotely execute python code from your non-android computer (such as linux, windows...).
- SL4A installation steps are introduced here
- RemoteControl setup steps are described here
- SL4A API is also described here
* Get location and geocode from android device (RemoteControl)
yaboo@maniac:~/Downloads/android-sdk-linux_x86/platform-tools$ python
Python 2.6.5 (r265:79063, Apr 16 2010, 13:57:41)
[GCC 4.4.3] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import android
>>> droid = android.Android(('192.168.10.4', 46522)) # public server mode
>>> droid.startLocating()
Result(id=0, result=None, error=None)
>>> loc = droid.readLocation().result
>>> loc
{u'network': {u'altitude': 0, u'provider': u'network', u'longitude': 139.***69349999998, u'time': 1311439075865, u'latitude': 35.***094566666668, u'speed': 0, u'accuracy': 75}, u'gps': {u'altitude': 58.9000244140625, u'provider': u'gps', u'longitude': 139.***20321081579, u'time': 1311439081000, u'latitude': 35.***270288087428, u'speed': 0, u'accuracy': 55}}
>>> n = loc['network']
>>> la = n['latitude']
>>> lo = n['longitude']
>>> la
35.***094566666668
>>> lo
139.***69349999998
>>> address = droid.geocode(la, lo).result
>>> print repr(address).decode('unicode-escape')
[{u'thoroughfare': u'*丁目', u'locality': u'**市', u'admin_area': u'**県', u'feature_name': u'27', u'country_code': u'JP', u'country_name': u'日本'}]
>>> droid.stopLocating()
Result(id=3, result=None, error=None)
* Testing TelephonyManager functionality
>>> print droid.getDeviceId().result
3568***********
>>> print droid.getCellLocation().result
{u'lac': 145, u'cid': 99008715}
>>> print droid.getDeviceSoftwareVersion().result
01
>>> print droid.getNeighboringCellInfo().result
[]
>>> print droid.getNetworkOperator().result
44010
>>> print droid.getNetworkOperatorName().result
NTT DOCOMO
>>> print droid.getPhoneType().result
gsm
>>> print droid.getSimCountryIso().result
jp
>>> print droid.getSimOperator().result
44010
>>> print droid.getSimOperatorName().result
>>> print droid.getSimSerialNumber().result
89811**************
>>> print droid.getSimState().result
ready
>>> print droid.SubscriberId().result
com.googlecode.android_scripting.rpc.RpcError: Unknown RPC.
None
* Testing Batterymanager API
>>> droid.batteryStartMonitoring()
Result(id=24, result=None, error=None)
>>> print droid.batteryCheckPresent().result
True
>>> print droid.batteryGetHealth().result
2
>>> print droid.batteryGetLevel().result
74
>>> print droid.batteryGetPlugType().result
2
>>> print droid.batteryGetPlugType().result
1
>>> print droid.batteryGetStatus().result
2
>>> print droid.batteryGetTechnology().result
Li-ion
>>> print droid.batteryGetTemperature().result
360
>>> print droid.batteryGetVoltage().result
4057
>>> print droid.readBatteryData().result
{u'status': 2, u'temperature': 380, u'level': 74, u'battery_present': True, u'plugged': 1, u'health': 2, u'voltage': 4057, u'technology': u'Li-ion'}
>>> droid.batteryStopMonitoring()
Result(id=35, result=None, error=None)
* Testing CommonIntentsFacade
>>> droid.viewMap(u"*****") # android device open google map!!! Result(id=40, result=None, error=None)
* Testing ContactsFacade
>>> droid.contactsGetCount().result 301
* Testing WifiFacade
>>> print droid.wifiGetConnectionInfo().result
{u'ssid': u'**********', u'bssid': u'00:0d:02:f7:**:**', u'network_id': 0, u'supplicant_state': u'completed', u'link_speed': 54, u'mac_address': u'04:**:65:**:**:18', u'rssi': -57, u'ip_address': 67***24, u'hidden_ssid': False}
>>> print droid.wifiGetScanResults().result
[{u'capabilities': u'[WPA-PSK-TKIP+CCMP][WPA2-PSK-TKIP+CCMP]', u'frequency': 2467, u'ssid': u'logitec51', u'bssid': u'00:01:8e:f2:**:c0', u'level': -82}, {u'capabilities': u'[WEP]', u'frequency': 2442, u'ssid': u'**********', u'bssid': u'00:0d:02:f7:c0:bc', u'level': -55}]
python tips: print list contains japanese characters
>>> L = [u"ほげ", u"まげ"]
>>> L
[u'\u307b\u3052', u'\u307e\u3052']
>>> print repr(L).decode('unicode-escape')
[u'ほげ', u'まげ']
>>>
2011/07/23
python tips: creating polar graph using matplotlib
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
import csv
import codecs
import matplotlib
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure, show, rc, grid
def main():
argvs = sys.argv
argc = len(argvs)
if (argc != 4):
print "Usage: python %s input_file output_file title" %(argvs[0])
sys.exit(0)
in_file = argvs[1]
out_file = argvs[2]
title = argvs[3]
csvfile = codecs.open(in_file, 'r', 'utf-8')
list_x = []
list_y = []
for row in csv.reader(csvfile):
radian = 0
if float(row[0]) < 0:
radian = (float(row[0])+360.0)/180
else:
radian = float(row[0])/180
list_x.append(np.pi*radian)
list_y.append(float(row[1]))
init_graph_settings()
draw_polar_graph(list_x, list_y, out_file, title)
csvfile.close()
def init_graph_settings():
# radar green, solid grid lines
rc('grid', color='#316931', linewidth=0.5, linestyle='--')
rc('xtick', labelsize=15)
rc('ytick', labelsize=10)
def draw_polar_graph(list_x, list_y, out_file, title):
"""
draws polar graph
:param list_x: list contains x values
:param list_y: list contains y values
:param title: title for a graph
:type list_x: list contains float values
:type list_y: list contains float values
:type title: string.
"""
# force square figure and square axes looks better for polar, IMO
width, height = matplotlib.rcParams['figure.figsize']
size = min(width, height)
# make a square figure
fig = figure(figsize=(size, size))
ax = fig.add_axes([0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8], polar=True, axisbg='#d5de9c')
ax.plot(list_x, list_y, 'r.', markersize=2)
ax.set_rmax(10000.0)
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=20)
grid(True)
fig.savefig(out_file, dpi=100)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
2011/07/22
sphinx tips: sphinx.ext.pngmath plugin
Below is a sample code for checking how sphinx pngmath plugin works. If you ompile below code and check output with browser, you can see TeX like expression is converted to mathematical expression. You need to install dvipng for using pngmath plugin :-)
====================
sphinx.ext.math test
====================
.. math::
(a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2
(a - b)^2 = a^2 - 2ab + b^2
.. math::
(a + b)^2 &= (a + b)(a + b) \\
&= a^2 + 2ab + b^2
.. math:: (a + b)^2 = a^2 + 2ab + b^2
python tips: googley style docstring
I surveyed some comment style in python. One is sphinx style and the other is google style (they are introduced in this site). However sphinx style is suitable for documentation using sphinx, its code legibility is poorer than google style. Below code is commented in google style.
#!/usr/bin/env python
#
# Copyright 2011 Yuki OYABU Inc.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
def fetch_bigtable_rows(big_table, keys, other_silly_variable=None):
"""
Fetches rows from a Bigtable.
Retrieves rows pertaining to the given keys from the Table instance
represented by big_table. Silly things may happen if
oahter_silly_variable is not None.
Args:
big_table:
An open Bigtable Table instance.
keys:
A sequence of strings representing the key of each table
row to fetch.
other_silly_variable:
Another optional variable, that has a much longer name than
the other args, and which does nothing.
Returns:
A dict mapping keys to the corresponding table row data
fetched. Each row is represented as a tuple of strings. For
example::
{'Serak' : ('Rigel VII', 'Preparer'),
'Zim': ('Irk', 'Invader'),
'Lrrr': ('Omicron Persei 8', 'Emperor')}
If a key from the keys argument is missing from the dictionary,
then that row was not found in the table.
Raises:
IOError:
An error occured accessing the bigtable. Table object.
"""
pass
class SampleClass(object):
"""
Summary of class here.
Longer class information....
Longer class information....
Attributes:
likes_spam:
A boolean indicating if we like SPAM or not.
eggs:
An integer count of the eggs we have laid.
"""
def __init__(self, likes_spam=False):
"""Inits SampleClass with blah."""
self.likes_spam = likes_spam
self.eggs = 0
def public_method(self):
"""Performs operation blah."""
2011/07/16
ubuntu tips: how to add repository using apt-key
sometime i cannot access to keyserver.ubuntu.com, and cannnot automatically update my package repository using add-repository command. here I show you how manually update my package repogitory.
# get gpgkey from anywhere...
> sudo apt-key add ${gpgkey_file}
# edit /etc/apt/sources.list for update repositories
> sudo apt-get update
shpinx tips: avoid ExtBabel class error for compiling japanese latex
i don't know why below error occurs...
modify /usr/local/lib/python2.6/dist-packages/Sphinx-1.0.7-py2.6.egg/sphinx/writers/latex.py
(just comment out non-japanese process....)
yaboo@sp2:~/DocProject$ make latex
sphinx-build -b latex -d _build/doctrees . _build/latex
Running Sphinx v1.0.7
loading translations [ja]... done
loading pickled environment... done
building [latex]: all documents
updating environment: 0 added, 0 changed, 0 removed
looking for now-outdated files... none found
processing testProject.tex... index intro code bd sd
resolving references...
writing...
Exception occurred:
File "/usr/local/lib/python2.6/dist-packages/Sphinx-1.0.7-py2.6.egg/sphinx/writers/latex.py", line 193, in __init__
babel = ExtBabel(builder.config.language)
TypeError: __init__() takes exactly 3 arguments (2 given)
The full traceback has been saved in /tmp/sphinx-err-q8bibE.log, if you want to report the issue to the developers.
Please also report this if it was a user error, so that a better error message can be provided next time.
Either send bugs to the mailing list at modify /usr/local/lib/python2.6/dist-packages/Sphinx-1.0.7-py2.6.egg/sphinx/writers/latex.py
(just comment out non-japanese process....)
if builder.config.language:
self.elements['classoptions'] += ',english,dvipdfm'
self.elements['babel'] += r'\newcount\pdfoutput\pdfoutput=0'
self.elements['preamble'] += \
r'\AtBeginDvi{\special{pdf:tounicode EUC-UCS2}}'
self.elements['shorthandoff'] = ''
self.elements['fncychap'] = '\\usepackage[Sonny]{fncychap}'
else:
sphinx tips: sphinx extenstions and configurations
# Abstraction
I installed blockdiag and seqdiag provided by tk0miya.This post show you how to install and setup *diag tools and autodoc.
# blockdiag and seqdiag installation
- blockdiag installation
sudo easy_install sphinx
sudo easy_install blockdiag sudo easy_install sphinxcontrib-blockdiag- seqdiag installation
sudo easy_install seqdiag sudo easy_install sphinxcontrib-seqdiag# additional settings into conf.py
# Enabled extensions (blockdiag and seqdiag, autodoc!)
extensions = ['sphinxcontrib.blockdiag','sphinxcontrib.seqdiag','sphinx.ext.autodoc']
# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('./codes'))
# configure default autodoc's action
autodoc_default_flags = ['members', 'undoc-members', 'show-inheritance']
# Fontpath for blockdiag (truetype font)
blockdiag_fontpath = '/usr/share/fonts/truetype/ipafont/ipagp.ttf'
blockdiag_tex_image_format = 'PNG'
# Fontpath for seqdiag (truetype font)
seqdiag_fontpath = '/usr/share/fonts/truetype/ipafont/ipagp.ttf'
seqdiag_tex_image_format = 'PNG'
2011/07/15
sphinx tips: useful links
sphinx is "python documentation generation" tool.
sphinx is one of powerful documentation tool I have ever used.
Here, I list useful link how to use sphinx and reStructuredText.
sphinxreStructuredText
reStructuredText add-on
sphinx is one of powerful documentation tool I have ever used.
Here, I list useful link how to use sphinx and reStructuredText.
sphinxreStructuredText
reStructuredText add-on
latex tips: texlive2010 installation
ラベル:
latex
Download texlive2010 iso image from a nearest CTAN site
http://ftp.yz.yamagata-u.ac.jp/pub/CTAN/systems/texlive/Images/
Mount the iso image like this:
http://ftp.yz.yamagata-u.ac.jp/pub/CTAN/systems/texlive/Images/
Mount the iso image like this:
sudo mount -o loop texlive2010-20100826.iso /mnt3Install texlive2010
cd /mnt3
sudo sh install-tl
2011/07/14
python tips: draw gaussian pdf graph with matplotlib
*** Definition of gaussian distribution ***
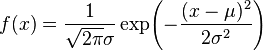
*** Sample code for drawing gaussian distribution ***
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
import pylab as pl
import numpy as np
from enthought.mayavi import mlab
def gauss2d(x):
return 1/np.sqrt(2*np.pi) * np.exp(-(x**2)/2)
def gauss3d(x, y):
return 1/np.sqrt(2*np.pi) * np.exp(-(x**2 + y**2)/2)
def plot_gauss2d():
x = np.mgrid[-4:4:100j]
# matplotlib functions
pl.plot(gauss2d(x), 'bo-')
pl.ylabel('gauss2d(x)')
pl.xlabel('x')
pl.show()
def plot_gauss3d():
x, y = np.mgrid[-4:4:100j, -4:4:100j]
"""
x, y = np.mgrid[-2:2:5j, -2:2:5j]
array([[[-2., -2., -2., -2., -2.],
[-1., -1., -1., -1., -1.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[ 2., 2., 2., 2., 2.]],
[[-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.],
[-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.],
[-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.],
[-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.],
[-2., -1., 0., 1., 2.]]])
x[0,0] ==> -2.0
y[0,0] ==> -2.0
"""
# matplotlib functions
pl.plot(gauss3d(x, y))
pl.ylabel('gauss3d(x)')
pl.xlabel('x')
pl.show()
def plot_gauss3d_mayavi():
x, y = np.mgrid[-4:4:100j, -4:4:100j]
z = gauss3d(x, y)
mlab.surf(z, warp_scale='auto')
mlab.outline()
mlab.axes()
mlab.show()
def main():
#plot_gauss2d()
#plot_gauss3d()
plot_gauss3d_mayavi()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
*** Sample code output ***
- output from gauss2d function

- output from gauss3d function

- output from gauss3d_mayavi function

2011/07/13
python tips: matplotlib plot option
ラベル:
python
#/usr/bin/env python
# coding:utf-8
import pg
import sys
import datetime
from pylab import *
def main():
argvs = sys.argv
argc = len(argvs)
""" check argument """
if (argc != 1 + 6):
argument = "dbname dbuser dbpass fromdate todate dbtable_prefix"
print "Usage: python %s %s" % (argvs[0], argument)
sys.exit(1)
dbname=argvs[1]
dbuser=argvs[2]
dbpass=argvs[3]
fromdate=argvs[4]
todate=argvs[5]
prefix=argvs[6]
""" initialization """
initGraphParams()
dbobj = getConnection(dbname, dbuser, dbpass)
""" get X label """
Lx = makeX(fromdate, todate)
Lx2 = makeX2(fromdate, todate)
""" get X,Y data """
classes = getClassId()
styles = ('-', 'x-', '+-', '*-')
colors = ('b', 'g', 'r', 'c', 'm', 'y', 'k')
count = 0
for cls in classes:
Ly = makeY(dbobj, Lx, prefix, 'class', cls, 'rows')
style = styles[count % len(styles)]
color = colors[count % len(colors)]
plot(Lx2, Ly, style+color, label=cls)
count += 1
title('number of XXX')
xlabel('date')
ylabel('number')
grid(True)
legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.01, 1), loc=2, ncol=2, borderaxespad=0.)
show()
dbobj.close()
python tips: create line graph with matplotlib
*** sample code (mypg.py) ***
*** output from above code ***

*** matplotlib reference pages ***
ぐうたらの部屋
Matplotlib サンプル集 - Kaiseki
http://www.ike-dyn.ritsumei.ac.jp/~uchida/scipy-lecture-notes/intro/index.html
#/usr/bin/env python
# coding:utf-8
# need to install python-pygresql
import pg
import sys
from pylab import *
def main():
argvs = sys.argv
argc = len(argvs)
# check argument
if (argc != 4):
print "Usage: python %s dbname dbuser dbpass" % (argvs[0])
sys.exit(1)
dbname=argvs[1]
dbuser=argvs[2]
dbpass=argvs[3]
dbobj = getConnection(dbname, dbuser, dbpass)
# input data from database tables
Lx = getValueX()
L1 = collectData(dbobj, '1')
L2 = collectData(dbobj, '2')
L3 = collectData(dbobj, '3')
L4 = collectData(dbobj, '4')
# plot data using matplotlib
plot(Lx, L1, label='id=1')
plot(Lx, L2, label='id=2')
plot(Lx, L3, label='id=3')
plot(Lx, L4, label='id=4')
# set labels and title
xlabel('hour')
ylabel('random_value')
title('plot test')
# draw legend
legend()
# draw graph
show()
dbobj.close()
def getValueX():
L = []
hour = 0
while (hour <= 23):
L.append(hour)
hour += 1
return L
# collecting data if same id
def collectData(dbobj, target):
L = []
sn = 0
while sn <= 23:
dbtable='public.table_' + str(sn)
sql="SELECT * FROM %s WHERE id = '%s';" % (dbtable, target)
for row in dbobj.query(sql).dictresult():
if row['id'] == target:
L.append(int(row['value']))
sn += 1
return L
# debug function
def showTables(dbobj):
for tbl in dbobj.get_tables():
print tbl
# initialize db connection
def getConnection(dbname, dbuser, dbpass):
pg.set_defhost('localhost')
pg.set_defport(5432)
pg.set_defbase(dbname)
return pg.DB(user=dbuser, passwd=dbpass)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
*** output from above code ***
yaboo@maniac:~/$ python mypg.py mydb test test

*** matplotlib reference pages ***
ぐうたらの部屋
Matplotlib サンプル集 - Kaiseki
http://www.ike-dyn.ritsumei.ac.jp/~uchida/scipy-lecture-notes/intro/index.html
shell script tips: bash and function
*** motivation ***
sh script does not have ${RANDOM} value which generates random value if used in bash script. Below is sample code explains how to use ${RANDOM} and define functions in bash scripts.
*** sample code (makeData.sh) ***
sh script does not have ${RANDOM} value which generates random value if used in bash script. Below is sample code explains how to use ${RANDOM} and define functions in bash scripts.
*** sample code (makeData.sh) ***
#!/bin/bash*** output from above script ***
function create_db(){
dbname=$1
dbuser=$2
dbpass=$3
PGPASSWORD=${dbpass} dropdb -U ${dbuser} ${dbname}
PGPASSWORD=${dbpass} createdb -U ${dbuser} ${dbname}
}
function create_tbl(){
id=0
dbname=$1
dbuser=$2
dbpass=$3
dbtable=$4
sql="CREATE TABLE ${dbtable} (id text, value int);"
PGPASSWORD=${dbpass} psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -c "${sql}"
while [ ${id} -le 3 ]
do
id=`expr ${id} + 1`
sql="INSERT INTO ${dbtable} VALUES (${id}, ${RANDOM});"
PGPASSWORD=${dbpass} psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -c "${sql}"
done
}
function select_tbl(){
dbname=$1
dbuser=$2
dbpass=$3
dbtable=$4
sql="SELECT * FROM ${dbtable};"
PGPASSWORD=${dbpass} psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -q -c "${sql}"
}
function main(){
dbname=$1
dbuser=$2
dbpass=$3
create_db ${dbname} ${dbuser} ${dbpass}
sn=0
prefix="table_"
while [ ${sn} -le 23 ]
do
dbtable=${prefix}${sn}
create_tbl ${dbname} ${dbuser} ${dbpass} ${dbtable}
select_tbl ${dbname} ${dbuser} ${dbpass} ${dbtable}
sn=`expr ${sn} + 1`
done
}
# Program starts here!!!
if [ $# -ne 3 ]; then
echo "usage: bash $0 dbname dbuser dbpass"
exit
fi
main $1 $2 $3
yaboo@maniac:~$ bash makeData.sh mydb test test
id | value
----+-------
1 | 632
2 | 5999
3 | 3495
4 | 3127
(4 行)
id | value
----+-------
1 | 29475
2 | 7581
3 | 17044
4 | 12726
(4 行)
id | value
----+-------
1 | 13619
2 | 25982
3 | 21835
4 | 23054
(4 行)
id | value
----+-------
1 | 726
2 | 15405
3 | 16549
4 | 16405
(4 行)
id | value
----+-------
1 | 14362
2 | 22030
3 | 16364
4 | 24379
(4 行)
...
id | value
----+-------
1 | 8468
2 | 10413
3 | 12345
4 | 30637
(4 行)
id | value
----+-------
1 | 8372
2 | 16466
3 | 31683
4 | 23073
(4 行)
yaboo@maniac:~$
2011/07/12
postgres tips: enable md5 authentication
step1. Add user
[default configuration]
postgres@maniac:~$ createuser teststep2. Set password for user
新しいロールをスーパーユーザとしますか? (y/n) n
新しいロールにデータベース作成権限を与えますか? (y/n) y
新しいロールにロールを作成する権限を与えますか? (y/n) y
postgres@maniac:~$ psqlstep3. Edit pg_hba.conf (hba: host based authentication)
psql (8.4.8)
"help" でヘルプを表示します.
postgres=# alter user postgres with encrypted password 'test';
ALTER ROLE
[default configuration]
# Database administrative login by UNIX sockets[configuration enables md5 authentication for user 'postgres']
local all postgres ident
# TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all ident
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 md5
# Database administrative login by UNIX socketsstep4. Restart postgresql
local all postgres ident
local all test md5
# TYPE DATABASE USER CIDR-ADDRESS METHOD
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all ident
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 md5
sudo /etc/init.d/postgresql-8.4 restart
* Restarting PostgreSQL 8.4 database server [ OK ]
yaboo@maniac:~$ createdb -U test sampledb
パスワード:
yaboo@maniac:~$ psql -U test sampledb
ユーザ test のパスワード:
psql (8.4.8)
"help" でヘルプを表示します.
sampledb=>
2011/07/11
postgres tips: copy and \copy
Below explanation is quoted from http://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/COPY
COPY is the Postgres method of data-loading. Postgres's COPY comes in two separate variants, COPY and \COPY: COPY is server based, \COPY is client based.
COPY will be run by the PostgreSQL backend (user "postgres"). The backend user requires permissions to read & write to the data file in order to copy from/to it.You need to use an absolute pathname with COPY.
\COPY on the other hand, runs under the current $USER, and with that users environment. And \COPY can handle relative pathnames. The psql \COPY is accordingly much easier to use if it handles what you need.
COPY is the Postgres method of data-loading. Postgres's COPY comes in two separate variants, COPY and \COPY: COPY is server based, \COPY is client based.
COPY will be run by the PostgreSQL backend (user "postgres"). The backend user requires permissions to read & write to the data file in order to copy from/to it.You need to use an absolute pathname with COPY.
\COPY on the other hand, runs under the current $USER, and with that users environment. And \COPY can handle relative pathnames. The psql \COPY is accordingly much easier to use if it handles what you need.
postgres tips: How to Execute PostgreSQL Commands Inside Unix Shell Scripts
I've used to use -c option (method1) when execute postgreSQL command inside unix shell scripts. However, method1 supports single postgreSQL command and requires backslash '\' when postgreSQL is written by multiple lines. On the contrary, method2 supports multiple command at a time and does not require any backslash 8^). I think method2 is better than what I used to do(method1)
Method1: Using -c option
Method2: Using EOF operator
Method1: Using -c option
#!/bin/sh
dbname="mydb"
dbuser="postgres"
table1="test1"
table2="test2"
psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -c "
DROP TABLE ${table1};"
psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -c "
DROP TABLE ${table2};"
psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -c "
CREATE TABLE ${table1} \
(id int, \
name text);"
psql -U ${dbuser} -d ${dbname} -c "
CREATE TABLE ${table2} \
(id int, \
name text);"
Method2: Using EOF operator
#!/bin/sh
dbname="mydb"
dbuser="postgres"
table1="test1"
table2="test2"
psql -d ${dbname} -U ${dbuser} << EOF
DROP TABLE ${table1};
DROP TABLE ${table2};
CREATE TABLE ${table1}
(id int,
name text);
CREATE TABLE ${table2}
(id int,
name text);
EOF
2011/07/10
postgres tips: postgis operations
What is PostGIS?
PostGIS adds support for geographic objects to the PostgreSQL object-relational database. In effect, PostGIS "spatially enables" the PostgreSQL server, allowing it to be used as a backend spatial database for geographic information systems (GIS), much like ESRI's SDE or Oracle's Spatial extension
PostGIS Initialization
PostGIS Tips
1. Create geometry data from x, y
2. Create spatial index to geometry data
3. Create intersection and its area
PostGIS adds support for geographic objects to the PostgreSQL object-relational database. In effect, PostGIS "spatially enables" the PostgreSQL server, allowing it to be used as a backend spatial database for geographic information systems (GIS), much like ESRI's SDE or Oracle's Spatial extension
PostGIS Initialization
createdb ${dbname}
createlang plpgsql ${dbname}
psql -d ${dbname} -f /usr/share/postgresql/8.4/contrib/postgis-1.5/postgis.sql
psql -d ${dbname} -f /usr/share/postgresql/8.4/contrib/postgis-1.5/spatial_ref_sys.sql
psql -d ${dbname} -f /usr/share/postgresql/8.4/contrib/postgis_comments.sql
PostGIS Tips
1. Create geometry data from x, y
-- 4326 means WGS84
CREATE TABLE sample_data AS
SELECT
ST_GeomFromText('POINT('||x||' '||y||')', 4326) AS the_geom
FROM
${table}
2. Create spatial index to geometry data
-- GiST: Generalized Search Trees Indexes
CREATE INDEX
geom_index
ON
sample_data
USING GIST (the_geom);"
3. Create intersection and its area
-- intersection(geom_1, geom_2) returns intersection
CREATE TABLE intersections AS
SELECT
Area(intersection(a.the_geom, b.the_geom)) AS area,
intersection(a.the_geom, b.the_geom) AS the_geom
FROM
geom_data_1 as a
INNER JOIN
geom_data_2 as b
ON
ST_Intersects(a.the_geom, b.the_geom);
2011/07/08
shell script tips: date command
"date" command is useful when we write a shell script which does per-day-processing.
#/bin/sh
fromdate="20110101"
todate="20110501"
date=${fromdate}
while [ ${date} -le ${todate} ]
do
# do somewhat you want
date=`date -d "$(date +2011-06-30) +1 day" +%Y%m%d`
done
2011/07/02
Usage of optparse
Sample code for optparse [sample_code.py]
Testing above sample code
from optparse import OptionParser
def main():
usage = "usage: %prog [options] something"
parser = OptionParser(usage)
parser.add_option("-f", "--file",
default=None, dest="filename",
help="read data from FILENAME")
parser.add_option("-v", "--verbose",
default=True, action="store_true", dest="verbose",
help="verbose output")
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
if len(args) != 1:
parser.error("incorrect number of arguments")
if options.verbose:
print "reading %s..." % options.filename
print options.verbose
print options.filename
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Testing above sample code
# python sample_code.py something
reading None...
True
None
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
